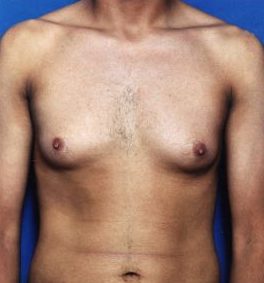
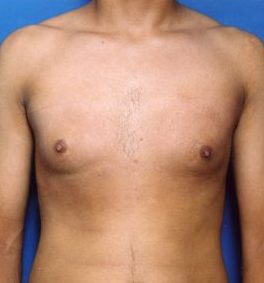
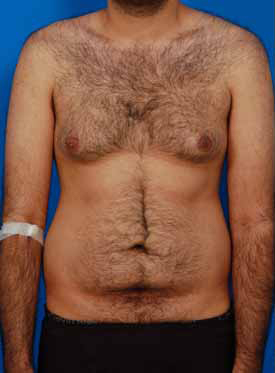
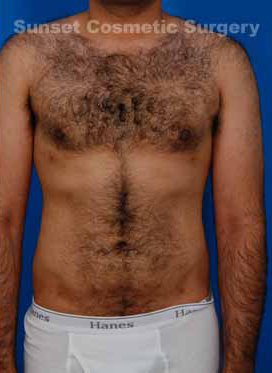
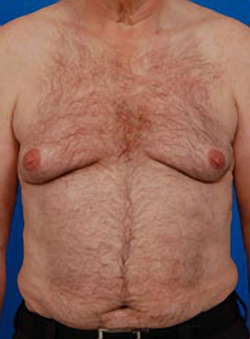
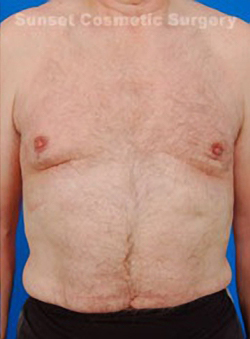
More About Gynecomastia and Surgery
Breast development is not uncommon for adolescent boys, when wild hormones and weight fluctuations can cause significant physical changes. These enlarged breasts may go away on their own, or they may remain for quite some time. Adult men can develop breasts for the same reasons, triggered by weight gain, internal chemical changes, or both.
Unwanted breasts that are made up of fatty tissue can be corrected with liposuction, which removes only the fat in your breasts. Sometimes this type of procedure can be done under a local anesthetic rather then a general anesthetic.
More involved gynecomastia surgery is needed for breasts that have grown to include not just fat, but glandular tissue as well. These glands are more firm and must be cut out, and any related fat can be removed via suction.
In some cases, men have gained and then lost a significant amount of weight, leading to sagging, deflated breasts that cover up an otherwise slim and trim chest. Excess, stretched-out skin can be removed in another form of gynecomastia surgery called mastopexy.
In many cases, any necessary incisions are made in the line between the areola (the dark skin around the nipple) and the rest of the chest where skin changes from darker to lighter tones. This allows the doctor access to the tissues to be repositioned or removed, but camouflages any resulting scar.
The average gynecomastia surgery takes only a couple of hours, and recovery takes approximately a week, depending on the patient. Bruising and swelling will appear at first, but will fade in the days after your surgery. Even then, patients are advised to avoid rigorous physical activity for about a month.
The specific gynecomastia surgery best for you will depend on your individual situation, body type, and aesthetic desires for your chest and body.